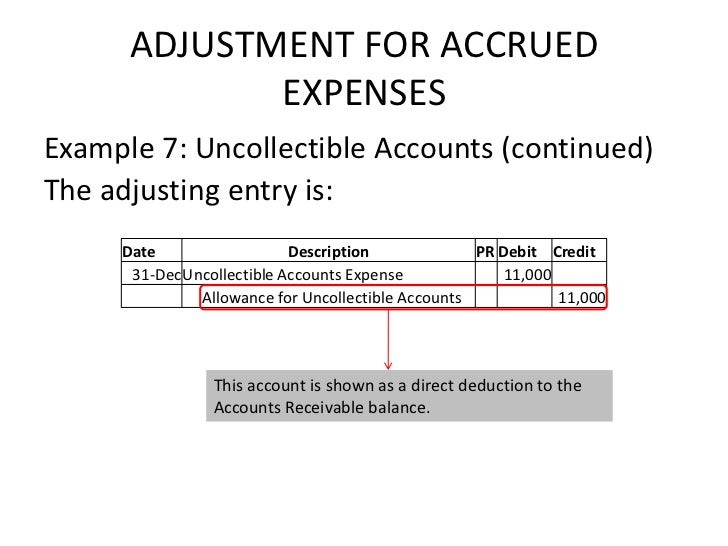
-Hallo friends, Accounting Methods, in the article you read this time with the title Uncollectible Accounts Adjusting Entry, we have prepared this article well for you to read and retrieve the information therein.
Hopefully the content of article posts Uncollectible, which we write this you can understand. Alright, happy reading.
Title : Uncollectible Accounts Adjusting Entry
link : Uncollectible Accounts Adjusting Entry
Uncollectible Accounts Adjusting Entry
The two accounts affected by this entry contain this information: note that prior to the august 24 entry of $1,400 to write off the uncollectible amount, the net realizable value of the accounts receivables was $230,000 ($240,000 debit balance in accounts receivable and $10,000 credit balance in allowance for doubtful accounts). Assuming that instead of basing the provision for uncollectible accounts on an analysis of receivables the adjusting entry on december 31 had been based on an estimated expense of 1⁄2 of 1% of the sales of $13,200,000 for the year, determine the following: a. bad debt expense for the year. The adjusting entry for uncollectible accounts does not affect the balance of the accounts receivable account false a business having a $300. 00 credit balance in allowance for uncollectible accounts and estimating its uncollectible accounts to be $4,000. 00 would record a $4,300. 00 credit to allowance for uncollectible accounts.
If you had $750 in uncollectible accounts, the adjusting entry is a debit to bad debt expense for $750 and a credit to allowance for doubtful accounts for $750. balance sheet and income summary both the allowance for doubtful accounts and bad debt expense are recorded on the financial statements. Sales on account are $250,000, so the estimate for uncollectible accounts is $5,000 ($250,000 x. 02). the journal entry to record this is to debit bad debt expense, an income statement account, and credit allowance for uncollectible accounts, a balance sheet contra-asset account for $5,000 each. If you had $750 in uncollectible accounts, the adjusting entry is a debit to bad debt expense for $750 and a credit to allowance for doubtful accounts for $750. balance sheet and income summary both the allowance for doubtful accounts and bad debt expense are recorded on the financial statements. Ex 9-12 entry for uncollectible accounts using the data in exercise 9-11, assume that the allowance for doubtful accounts for performance bike co. had a debit balance of $28,400 as of december 31. journalize the adjusting entry for uncollectible accounts uncollectible accounts adjusting entry as of december 31.
Writing off an account under the allowance method.
Adjustingentries For Uncollectible Accounts Small

Accounting For Uncollectible Receivables
Record the journal entry by debiting bad debt expense and crediting allowance for doubtful accounts. when you decide to write off an account, debit allowance for doubtful accounts allowance for doubtful accounts the allowance for doubtful accounts is a contra-asset account that is associated with accounts receivable uncollectible accounts adjusting entry and serves to reflect the.
Accounting For Uncollectible Receivables

Since the aging schedule approach is an alternative under the percentage-of-receivables method, the balance in the allowance account before adjustment affects the year-end adjusting entry amount recorded for uncollectible accounts. Accounting for uncollectible accounts receivable: as illustrated in the previous section, the estimation of uncollectible accounts receivable results in a journal entry in which uncollectible accounts expense is debited and the allowance for uncollectible accounts is credited. this entry reduces stockholders' equity and assets. Recorded adjusting entry for uncollectible accounts expense. journal: uncollectible accounts expense debit: uncollectible accounts expense credit: allowance for uncollectible accounts. wrote of sanderson company's past-due account as uncollectible. journal: uncollectible accounts expense.
Entries made under the allowance method subsequent to recording the annual adjusting entry are the same under either the direct or indirect approach to estimating the expense. whenever a specific account is uncollectible accounts adjusting entry identified as being uncollectible, it should be removed from the ledger with an entry such as this one recorded by sample company for one. An adjusting entry to recognize uncollectible accounts expense at december 31, 2014. an entry to write off accounts receivable at february 12, 2015. an adjusting entry to recognize uncollectible accounts expense at december 31, 2015. solution: (1). recognition of accounts receivable expense at december 31, 2014: (2). Accounting basics 02. debits and credits 03. chart of accounts 04. bookkeeping 05. accounting equation 06. accounting principles 07. financial accounting 08. adjusting entries 09. financial statements 10. balance sheet 11. working capital and liquidity 12. income statement 13. cash flow statement 14. financial ratios 15.
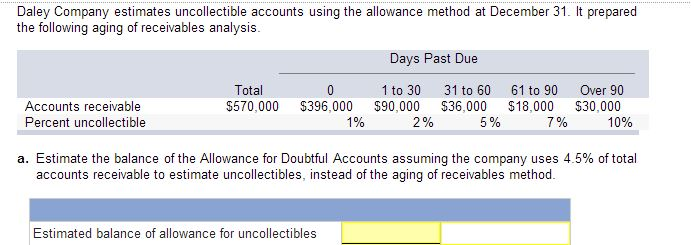
Percentage of accounts receivable method example. suppose based on past experience, 5% of the accounts receivable balance has been uncollectible, and the accounts receivable at the end of the current accounting period is 150,000, then the allowance for doubtful accounts in the balance sheet at the end of the accounting period would be calculated using this allowance method as follows:. There are several methods in estimating doubtful accounts. the estimates are often based on the company's past experiences. to recognize doubtful accounts or bad debts, an adjusting entry must be made at the end of the period. the adjusting entry for bad debts looks like this:. Debit: accounts receivable/notes receivable credit: allowance for uncollectible accounts received cash in full payment of sanderson company's account, previously written off as uncollectible (second entry).
A account receivable that has previously been written off may subsequently be recovered in full or in part. it is known as recovery of uncollectible accounts or recovery of bad debts. this article briefly explains the accounting treatment when a previously written off account is recovered and the uncollectible accounts adjusting entry cash is received from the related receivable. See more videos for uncollectible accounts adjusting entry. Allowance for doubtful accounts journal entry. to predict your company’s bad debts, you must create an allowance for doubtful accounts entry. you must also use another entry, bad debts expense, to balance your books. increase your bad debts expense by debiting the account, and decrease your ada account by crediting it.
Notice that the preceding entry reduces the receivables balance for the item that is uncollectible. the offsetting debit is to an expense account: uncollectible accounts expense. while the direct write-off method is simple, it is only acceptable in those cases where bad debts are immaterial in amount. The analysis shows that $1,800 would be required in the allowance for uncollectible accounts at the end of the period. if the allowance for uncollectible accounts has a credit balance of $200. the adjusting entry at the end of the year would be:. On january 1, 2005, the allowance for doubtful accounts had a credit balance of $2400. during 2005, abc wrote-off accounts receivable totaling $1,800 and made credit sales of $100,000. after the adjusting entry, the december 31, 2005, balance in the uncollectible accounts expense would be. Accounts receivable was credited in the above journal entry because accounts receivable are assets and assets decrease with credits. the allowance for uncollectible accounts was debited in the above journal entry because this account represents an estimate of accounts receivable that will not be collected.
A simple method to account for uncollectible accounts is the direct write-off approach. under this technique, a specific account receivable is removed from the accounting records at the time it is finally determined to be uncollectible. the appropriate entry for the direct write-off approach is as follows:. To recognize doubtful accounts or bad debts, an adjusting entry must be made at the end of the period. the adjusting entry for bad debts looks like this: dec 31: bad debts expense: on the other hand, is the uncollectible portion of the entire accounts receivable. Above, we assumed that the allowance for doubtful accounts began with a balance of zero. if instead, the allowance for uncollectible accounts began with a balance of $10,000 in june, we would make the following adjusting entry instead: $50,000 $10,000 = $40,000 (adjusting entry).