-Hallo friends, Accounting Methods, in the article you read this time with the title How To Calculate Variable Costs Using The Smallest Quadratic Method, we have prepared this article well for you to read and retrieve the information therein.
Hopefully the content of article posts Calculate, article posts Costs, article posts How To Calculate Variable Costs Using The Smallest Quadratic Method, article posts Method, article posts Quadratic, article posts Smallest, article posts Using, article posts Variable, which we write this you can understand. Alright, happy reading.
Title : How To Calculate Variable Costs Using The Smallest Quadratic Method
link : How To Calculate Variable Costs Using The Smallest Quadratic Method
How To Calculate Variable Costs Using The Smallest Quadratic Method
In accounting, to find the average cost, divide the sum of variable costs and fixed costs by the quantity of units produced. it is also a method for valuing inventory. in this sense, compute it as cost of goods available for sale divided by the number of units available for sale. Looking into differential calculus, we get the following normal equations: using the normal equations and the process of elimination we can derive a formula for b. we use this formula to calculate the variable costs when we apply the least-squares method: after calculating the variable costs (b) per unit, we can then compute the fixed costs via the formula: notice the accents above y and x. we use the means of the two variables. to calculate those we sum the variables in all observable data points and divide them by the number of data points, or we derive a simple average: changing the means in the formula above with those formulas, we get an how to calculate variable costs using the smallest quadratic method extended formula for the fixed costs: if we look at a graphical representation of the linear cost function, a is what we call the y-intercept of the line and equals the approximate fixed costs at any activity level, and bis the slope of the line and represents the variable costs per unit. Ideally, this can be confirmed on a scatter graph. one of the simplest ways to analyze costs is to use the high-low method, a technique for separating the fixed and variable cost components of mixed costs. using the highest and lowest levels of activity and their associated costs, we are able to estimate the variable cost components of mixed costs.
Formula for variable costs total variable cost = total quantity of output x variable cost per unit of output variable vs fixed costs in decision-making costs incurred by businesses consist of fixed and variable costs. How to find maximum and minimum value of quadratic function using the vertex form of the function. the maximum and the minimum value of the quadratic function can be determined using the standard form of the function. it is also known as the vertex form of the quadratic function. this is an algebraic method and does not involve the use of graphs. Let us take a look at an example to see the least-squares regression model in action. we have the following data on the costs for producing the last ten batches of a product. the data points show us the unit volume of each batch and the corresponding production costs. next, we can plot the data on a scatter plot to see if it looks linear. as the data seems a bit dispersed, let us calculate it’s correlation. we get a 0. 64 correlation coefficient between volume of units and cost of production. usually we consider values between 0. 5 and 0. 7 to represent a moderate correlation. to calculate the regression formulas we discussed, we need to add two help columns and calculate x * y and x2for each batch. we also need the means for x (volume of units) and y (production costs). after we have calculated the supporting values, we can go ahead and calculate our b. it represents the variable costs in our cost model and is called a slope in statistics. having calculated the b of our model, we can If you have several costs that are in the future, you can find the present value of these costs. the present value of the costs are how much the costs are worth today. present value of costs takes into account a concept known as time value.
Quadratic Equation Solver Quadratic Formula Calculator Free
When you understand your insurance costs, you can make better decisions about the type of policy that's right for you and the kind of coverage you need. while this is true of all insurance, this guide highlights health insurance costs to il. See full list on educba. com. For each alternative method considered, the task force used regression analysis to examine the relationship between the volume of the hospital activity involved (independent variable) and the life-cycle (initial investment plus lifetime operation and maintenance) costs (dependent variable).
Modeling Revenue Costs And Profit
Although the high low method is easy to calculate and helps us in forecasting future costs, it is not very commonly used because it has certain limitations: 1. the first limitation is that this method assumes that there is a linear relationship between cost and activity which is not the case always. 2. secondly, it only assumes 2 activity levels and is not the correct representation of the entire data set. 3. if there are changes in fixed or variable cost with time, this method does not capture that. because of all those limitations, this method is not effective in producing accurate and precise results. Cost per unit = (total fixed costs + total variable costs) / total units produced. a successful business relies on being able to make a profit. for both product and service-based businesses, the cost per unit is a valuable calculation to make sure their costs are lower than what a unit sells for. F ≥ 0, r = rt > 0 are state cost, final state cost, and input cost matrices. an infinite-dimensional problem: (trajectory u : [0,t] → rm is variable) continuous time linear quadratic regulator 4–2. Office of the assistant secretary how to calculate variable costs using the smallest quadratic method for planning and evaluation office of the assistant secretary for planning and evaluation 08/01/2001 this section describes the creation of variables used in the analysis of this report. we group the variab.
Example of variable costs. let us consider a bakery that produces cakes. it costs $5 in raw materials and $20 in direct labor to bake one cake. in addition, there are fixed costs of $500 (the equipment used). to illustrate the concept, see the table below: note how the costs change as more cakes are produced. For a quadratic cost function it is possible to scale the design variables such that the condition number of the hessian matrix with respect to the new design variables, is unity (the condition number of a matrix is calculated as the ratio of the largest to the smallest eigenvalues of the matrix). the steepest descent method converges in only. The least-squares method has some advantages and disadvantages that make it more desirable in certain situations: (+) simplicity the method is easy to understand and perform; (+) it’s applicable in almost any situation honestly, it’s hard to think of a case where the least-squares method will be inapplicable; (+) the technique has a strong underlying theoretical foundation in statistics; (–) as we already noted, the method is susceptible to outliers, since the distance between data points and the cost function line are squared. (–) it has an inherent assumption that the two analyzed variables have at least some kind of correlation. (–) the least-squares method how to calculate variable costs using the smallest quadratic method might yield unreliable results when the data is not normally distributed. however, this can be mitigated by including more data points in our sample.
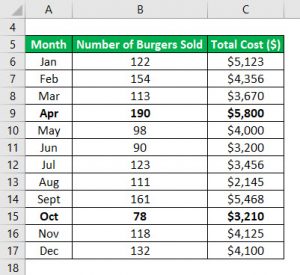
Fixed cost = lowest activity cost (variable cost per units * lowest activity units) fixed cost = $3,210($23. 125 * 78) fixed cost = $1,406. 25. so basically total cost equation is given by = 23. 125x + 1406. 25. where x is the number of burgers sold in a particular month. since you have the total cost equation now, you can use this to. The least-squares regression model is a statistical technique that may be used to estimate a linear total cost function for a mixed cost, based on past cost data. the function can then be used to forecast costs at different activity levels, as part of the budgeting process or to support decision-making processes. least-squares regression calculates a line of best fit to a set of data pairs, i. e. a series of activity levels and corresponding total costs. the idea behind the calculation is to minimize the sum of the squares of the vertical distances (errors) between data points and the cost function. in statistics, the lower error means better explanatory power of the regression model. the least squares model aims to define the line that minimizes how to calculate variable costs using the smallest quadratic method the sum of the squared errors. we are trying to determine the line that is closest to all observations at the same time. we need to be careful with outliers when applying the least-squares method, as it is sensitive to strange values pullin Here's how to calculate marginal cost, total cost, fixed cost, total variable cost, average total cost, average fixed cost, and average variable cost. there are many definitions relating to cost, including the following seven terms: the dat.
A quadratic equation is a polynomial equation that is of the form ax2+bx+c, where a, b and c are constant numbers, known as coefficients and x is the variable number. it is called as quadratic because the highest power of the variable (x) is 2 (x2) in the equation. it is to be noted that either of a, b and c can be zero and still the equation. See full list on magnimetrics. com. The least squares method is probably one of the most popular predictive analysis techniques in statistics. it is widely used to fit a function to a data set. the simplest example is defining a straight-line, as we looked above, but this function can be a curve or even a hyper-surface in multivariate statistical analysis. professionals apply the method in a variety of fields like medicine, biology, finance, agriculture, sociology, and others. thank you for reading and don’t forget to download the excel file below: the information and views set out in this publication are those of the author(s) and do not necessarily reflect the official opinion of magnimetrics. neither magnimetrics nor any person acting on their behalf may be held responsible for the use which may be made of the information contained herein. the information in this article is for educational purposes only and should not be treated as professional advice. magnimetrics accepts no responsibility for any damages or losse
A quadratic equation is an equation that can be written as ax ² + bx + c where a ≠ 0. in other words, a quadratic equation must have a squared term as its highest power. below how to calculate variable costs using the smallest quadratic method are the 4 methods to solve quadratic equations. click on any link to learn more about a method. the quadratic formula.