-Hallo friends, Accounting Methods, in the article you read this time with the title Under The Allowance Method Of Accounting For Uncollectible Accounts Bad Debts Expense Is Debited, we have prepared this article well for you to read and retrieve the information therein.
Hopefully the content of article posts accounting, article posts Accounts, article posts Allowance, article posts Debited, article posts Debts, article posts Expense, article posts Method, article posts Uncollectible, article posts Under, article posts Under The Allowance Method Of Accounting For Uncollectible Accounts Bad Debts Expense Is Debited, which we write this you can understand. Alright, happy reading.
Title : Under The Allowance Method Of Accounting For Uncollectible Accounts Bad Debts Expense Is Debited
link : Under The Allowance Method Of Accounting For Uncollectible Accounts Bad Debts Expense Is Debited
Under The Allowance Method Of Accounting For Uncollectible Accounts Bad Debts Expense Is Debited
Test 3 Flashcards Quizlet
Accounting 2010 Chapter 8 Quiz Flashcards Quizlet
Accounting 2010: chapter 8 quiz flashcards quizlet.
When a written of account is recovered, the first step is to reinstate it in the accounting record. the following journal entry is made for this purpose: notice that this entry is exactly the reverse of the entry that is made when an account receivable is written off. see uncollectible accounts expense allowance method. (2). Under the allowance method, if a specific customer's accounts receivable is identified as uncollectible, it is written off by removing the amount from accounts receivable. the entry to write off a bad account affects only balance sheet accounts: a debit to allowance for doubtful accounts and a credit to accounts receivable. Under the allowance method of calculating bad debts, there are two general ledger accounts bad debts, an expense account, and allowance for doubtful accounts, a contra-asset account used to offset to the accounts receivable balance. to record the bad debt expenses, you must debit bad debt expense and a credit allowance for doubtful accounts.
Chapter 9 Acct Multiple Choice Flashcards Quizlet
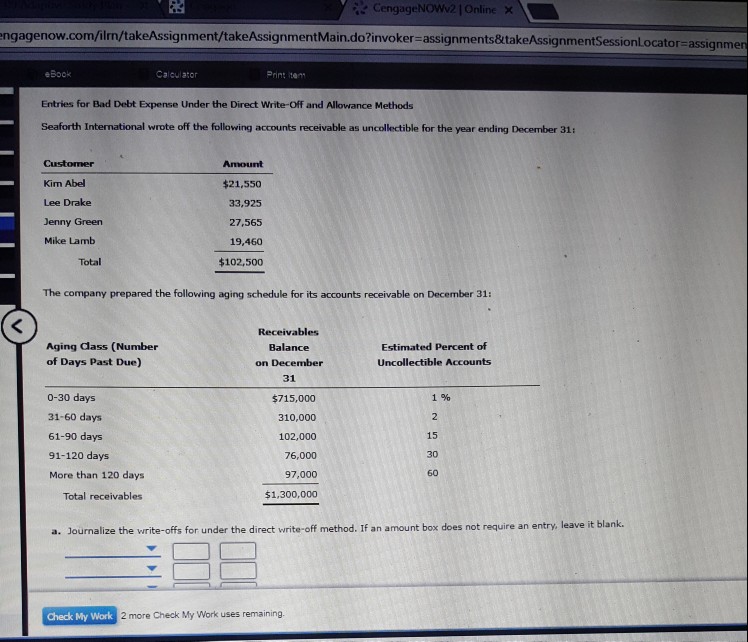
Under the direct write-off method of accounting for uncollectible accounts, bad debt expense is debited a. at the end of each accounting period. b. when a credit sale is past due. c. when an account is determined to be uncollectible & is written-off. d. whenever a pre-determined amount of credit sales have been made. In this example, estimated bad debts are $5,000. if the account has an existing credit balance of $400, the adjusting entry includes a $4,600 debit to bad debts expense and a $4,600 credit to allowance for bad debts. percentage of credit sales method. some companies estimate bad debts as a percentage of credit sales. The allowance method of accounting for bad debts involves estimating uncollectible accounts at the end of each period. it provides better matching of expenses and revenues on the income statement and ensures that receivables are stated at their cash (net) realizable value on the balance sheet.
How To Calculate Bad Debt Expenses
The allowancemethodof accounting for bad debts involves estimating uncollectible accounts at the end of each period. it provides better matching of expenses and revenues on the income statement and ensures that receivables are stated at their cash (net) realizable value on the balance sheet. cash (net) realizable value is the net amount of cash expected to be received. Chapter 8 reporting and analyzing receivables the allowance method is required for financial reporting purposes and has 3 essential features: 1. recording estimated uncollectible accounts: a. the amount of uncollectible a/r is estimated by ensuring that the balance in allowance for doubtful accounts is equal to the estimate of uncollectible accounts. any increase to the allowance balance is.
Chapter 8 Accounting Youll Remember Quizlet
Under this method of recognizing losses on credit sales, a contra asset account allowance for doubtful accounts is reported on the balance sheet. prior to specifically identifying an account receivable as uncollectible, a company debits bad debts expense and credits allowance for doubtful accounts for an estimated amount.
The bad debts under the allowance method of accounting for uncollectible accounts bad debts expense is debited expense remains at $10,000; it is not directly affected by the journal entry write-off. the bad debts expense recorded on june 30 and july 31 had anticipated a credit loss such as this. it would be double counting for gem to record both an anticipated estimate of a credit loss and the actual credit loss. When the allowance method is used to account for uncollectible accounts, bad debts expense is debited when a. a customer's account becomes past due b. an account becomes bad and is written off c. a sale is made d. management estimates the amount of uncollectibles. Direct write off method refers to the technique of accounting for the uncollectible accounts by businesses. under the direct write off method, once accounts are identified as uncollectible, the bad debts expense account is debited and the accounts receivable account is credited directly.
Underthe allowancemethod of calculating bad debts, there are two general ledger accounts bad debts, an expense account, and allowance for doubtful accounts, a contra-asset account used to offset to the accounts receivable balance. to record the bad debt expenses, you must debit bad debt expense and a credit allowance for doubtful accounts. When the allowance method is used to under the allowance method of accounting for uncollectible accounts bad debts expense is debited account for uncollectible accounts, bad debts expense is debited when management estimates the amount of uncollectibles the collection of an account that had been previously written off under the allowance method of accounting for uncollectibles. See full list on accountingcoach. com.
Required information under the allowance method, bad debts expense is recorded with an adjustment at the end of each accounting period that debits the bad debts expense account and credits the allowance for doubtful accounts. the uncollectible accounts are later written off with a debit to the allowance for doubtful accounts. on december 1. Under the direct write-off method of accounting for uncollectible accounts, bad debts expense is debited a. at the end of each accounting period b. when a credit sale is past due c. whenever a predetermined amount of credit sales have been made d. when an account is determined to be worthless. Let's illustrate the write-off with the following example. on june 3, a customer purchases $1,400 of goods on credit from gem merchandise co. on august 24, that same customer informs gem merchandise co. that it has filed for bankruptcy. the customer states that its bank has a lien on all of its assets. it also states that the liquidation value of those assets is less than the amount it owes the bank, and as a result gem will receive nothing toward its $1,400 accounts receivable. after confirming this information, gem concludes that it should remove, or write off, the customer's account balance of $1,400. under the allowance method of recording credit losses, gem's entry to write off the customer's account balance is as follows: note that prior to the august 24 entry of $1,400 to write off the uncollectible amount, the net realizable value of the accounts receivables was $230,000 ($240,000 debit balance in accounts receivable and $10,000 credit balance in allowance for doubtful accounts). after writing off the bad account on august 24, the net realizable value of the accounts receivable is still $230,000 ($238,600 debit balance in accounts receivable and $8,600 credit balance in allowance for doubtful accounts). after a seller has written off an accounts receivable, it is possible that the seller is paid part or all of the account balance that was written off. under the allowance method, if such a payment is received (whether directly from the customer or as a result of a court action) the seller will take the following two steps: for example, let's assume that a company prepares weekly financial statements. past experience indicates that 0. 3% of its sales on credit will never be collected. using the percentage of credit sales approach, this company automatically debits bad debts expense and credits allowance for doubtful accounts for 0. 3% of each week's credit sales. let's assume that in the current week this company sells $500,000 of goods on credit. it estimates its bad debts expense to be $1,500 (0. 003 x $500,000) and records the following journal entry:. Under the direct write-off method of accounting for uncollectible accounts, bad debts expense is debited a. at the end of each accounting period b. when a credit sale is past due c. whenever a predetermined amount of credit sales have been made d. when an account is determined to be worthless.
Under under the allowance method of accounting for uncollectible accounts bad debts expense is debited the allowance method, if a specific customer's accounts receivable is identified as uncollectible, it is written off by removing the amount from accounts receivable. the entry to write off a bad account affects only balance sheet accounts: a debit to allowance for doubtful accounts and a credit to accounts receivable. no expense or loss is reported on the income statement because this write-off is \\"covered\\" under the earlier adjusting entries for estimated bad debts expense. The seller's accounting records now show that the account receivable was paid, making it more likely that the seller might do future business with this customer. Another way sellers apply the allowance method of recording bad debts expense is by using the percentage of credit sales approach. this approach automatically expenses a percentage of its credit sales based on past history.