-Hallo friends, Accounting Methods, in the article you read this time with the title Uncollectible Accounts Percentage Of Sales, we have prepared this article well for you to read and retrieve the information therein.
Hopefully the content of article posts Uncollectible, which we write this you can understand. Alright, happy reading.
Title : Uncollectible Accounts Percentage Of Sales
link : Uncollectible Accounts Percentage Of Sales
Uncollectible Accounts Percentage Of Sales
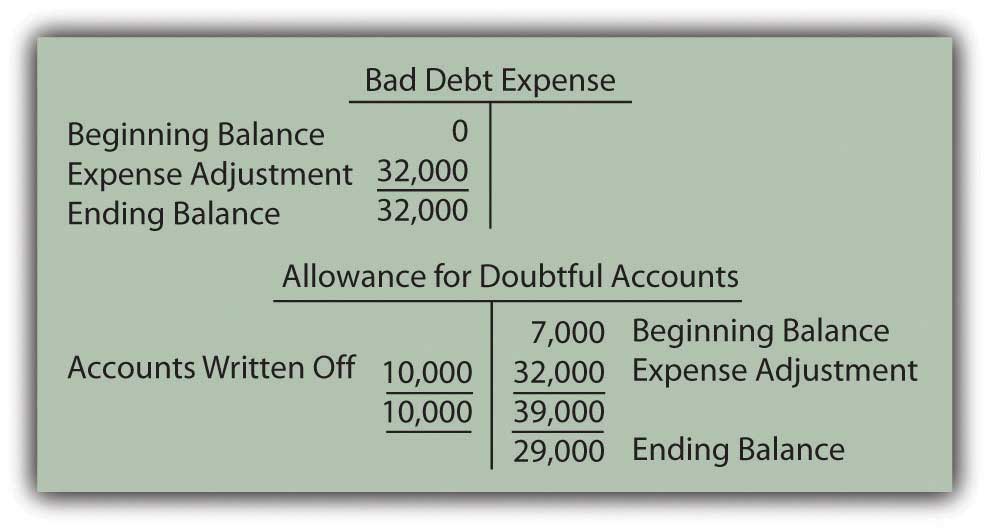
Bad Debts Expense Percentage Of Credit Sales Method Example
Mckinney & co. estimates its uncollectible accounts as a percentage of credit sales. mckinney made credit sales of $1,600,000 in 2016. mckinney estimates 3. 0% of its sales will be uncollectible. at the end of the first quarter of 2017, mckinney & co. reevaluates its receivables. Uncollectible accounts—percentage of sales and percentage of receivables at the end of the current year, the accounts receivable account of glenn’s nursery supplies has a debit balance of $390,000. credit sales are $2,800,000. record the end-of-period adjusting entry on december 31, in general journal form, for the estimated uncollectible accounts.
For example, if the company had january credit sales of $15,000, it could estimate its uncollectible accounts receivable to be $210 ($15,000 x. 014). the. 014 is the average percentage of uncollectible accounts receivable during year 1 through year 3. Sales on account are $250,000, so the estimate for uncollectible accounts is $5,000 ($250,000 x. 02). the journal entry to record this is to debit bad debt expense, an income statement account, and credit allowance for uncollectible accounts, a balance sheet contra-asset account for $5,000 each. Another way to estimate the amount of uncollectible accounts is to simply record a percentage of credit sales. for example, if your company and its industry has a long run experience of 0. 2% of credit sales being uncollectible, you might enter 0. 2% of each period's credit sales as a debit to bad debt expense and a credit to allowance for. Well, we take our net credit sales, multiply that by the percent uncollectible, so that our percentage estimate, to give us our allowance. so in this case, we take $100,000, that's our net credit sales, multiply that by our estimate of 2%, to give us an allowance of $2,000.
Estimating Bad Debts Financial Accounting
The percentage-of-sales method is commonly used to estimate the accounts receivable that a business expects will be uncollectible. when you use this method, use your small business’s past collection data to estimate what portion of the credit sales you generate each accounting period that will go unpaid. 1. 5% of sales when the basis for the allowance for doubtful account is on a percentage of sales, this is bad debts expense for the period. thus, entry will include a:. Using the percentage-of-sales method, the estimated total uncollectible accounts are $6,622. the allowance for uncollectible accounts prior to adjustment has a debit balance of $2,935. the accounts uncollectible accounts percentage of sales receivable balance is $44,420.
Percentage of sales method is an income statement approach for estimating bad debts expense. under this method bad debts expense is calculated as percentage of credit sales of the period. the percentage figure is calculated on the basis of past performance and other factors such as change in credit policy. The sales method (also referred to as income statement approach) estimates allowance for doubtful accounts using total credit sales for the period. under this approach, some percentage of the total credit sales for the period is determined to be uncollectible. commission (puc) today urged consumers, "to be conscious of utility account security when answering telemarketing sales calls from competitive energy suppliers (suppliers) and report
How to estimate uncollectible accounts dummies.
Accounting Flashcards Quizlet
The percentage-of-net-sales method is aimed at determining the amount of uncollectible accounts expense, and the aging method is aimed at determining the balance in the account allowance for uncollectible accounts. these methods thus will show different balances in both the expense and contra-asset accounts. Uncollectible accounts—percentage of sales and percentage of receivables. at the end of the current year, the accounts receivable account of parker's nursery supplies has a debit balance of $350,455. credit sales are $2,616,000. record the end-of-period adjusting entry on december 31, in uncollectible accounts percentage of sales general journal form, for the estimated uncollectible.
Solved Uncollectible Accountspercentage Of Sales And Per
Question: uncollectible accounts—percentage of sales and percentage of receivables at the end of the current year, the accounts receivable account of parker's nursery supplies has a debit balance of $350,455. credit sales are $2,616,000. record the end-of-period adjusting entry on december 31, in general journal form, for the estimated uncollectible accounts. Percentageof sales this method estimates the amount of bad debt expense a company will incur based on the amount of sales it receives. for example, if a business makes $100,000 in sales and estimates that 5 percent of sales is bad debts, then this would mean that approximately $5,000 should be added to the allowance for doubtful accounts. 2. explanation of percentage-of-sales approach percentage-of-sales approach (income statement approach) states that the amount of bad debt expense to be recognized by a company is calculated as a percentage of credit sales generated during the current accounting period. this approach does not consider the balance in the allowance for doubtful accounts because such balance is not used in the.
Calculate the sum of the amounts of each portion you expect will be uncollectible to calculate the total amount of uncollectible accounts. for example, calculate the sum of $750, $200, $1,050, $1,500 and $1,350. this equals $4,850 in uncollectible accounts. uncollectible accounts percentage of sales However, the company has chosen to use the percentage of receivables method rather than the percentage of sales method. officials have looked at all available evidence and come to the conclusion that 15 percent of ending accounts receivable ($160,000 × 15 percent or $24,000) is most likely to prove to be uncollectible.

On march 31, 2017, corporate finance institute reported net credit sales of $1,000,000. using the percentage of sales method, they estimated that 1% of their credit sales would be uncollectible. as you can see, $10,000 ($1,000,000 * 0. 01) is determined to be the bad debt expense that management estimates to incur. 2. percentage of receivables. The percentage-of-credit-sales method for estimating uncollectible accounts is sometimes described as: credit sales. the income statement approach for estimating bad debts uses a percentage of.
This page explains the use of sales method for estimating allowance for doubtful accounts. click here to read aging method.. the sales method (also referred to as income statement approach) estimates allowance for doubtful accounts using total credit sales for the period. under this approach, some percentage of the total credit sales for the period is determined to be uncollectible. When accounting for uncollectible receivables and using the percentage of sales method, the matching principle is violated. f at the end of a period (before adjustment), allowance for doubtful accounts has a credit balance of $250.
Estimating uncollectible accounts accountants use two basic methods to estimate uncollectible accounts for a period. the first method—percentage-of-sales method—focuses on the income statement and the relationship of uncollectible accounts to sales. Where the percentage of sales method looks at sales, the percentage of receivables method looks at the current amount of accounts receivable the business has accumulated at its point of calculation. the resulting figure indicates what the allowance for the doubtful accounts balance should be.