-Hallo friends, Accounting Methods, in the article you read this time with the title Uncollectible Accounts Percentage Of Sales, we have prepared this article well for you to read and retrieve the information therein.
Hopefully the content of article posts Uncollectible, which we write this you can understand. Alright, happy reading.
Title : Uncollectible Accounts Percentage Of Sales
link : Uncollectible Accounts Percentage Of Sales
Uncollectible Accounts Percentage Of Sales
Accounting Flashcards Quizlet
for rental to others and subsequently held for sale
Calculate allowance for doubtful accounts using sales method or income statement approach. prepare adjusting entry to recognize uncollectible accounts expense and to update the allowance for doubtful accounts account at the end of the year 2015. solution: (1). allowance for doubtful accounts: $175,000 × 0. 01 = $1,750 (2). Percentage of sales method for calculating doubtful accounts step 1. add together the credit sales your small business generated in each of the past three years. if you started your step 2. add together the amount of credit sales you failed to collect in each of the past three years. in this. Answer: according to the general ledger, the company generated $400,000 in credit sales during year two. if uncollectible accounts are expected to be 8 percent of that amount, the expense is reported as $32,000 ($400,000 × 8 percent). bad debt expense (the figure estimated) must be raised from its present zero balance to $32,000. Gaap requires that businesses extending credit to customers use the allowance method, which means they estimate uncollectible accounts. companies use a few different types of methods, usually based on their past experience with bad debt. for example, imagine that a company that’s been in business for five years has found that 2 percent of all credit sales will be uncollectible.
Percentageof Sales Method For Calculating Doubtful Accounts
Where the percentage of sales method looks at sales, the percentage of receivables method looks at the current amount of accounts receivable the business has accumulated at its point of calculation. the resulting figure indicates what the allowance for the doubtful accounts balance should be. The percentage of sales basis of estimating expected uncollectibles emphasizes the matching of expenses with revenues an aging of a company's accounts receivable indicates that $9,000 are estimated to be uncollectible. if allowance for doubtful accounts has a $1,100 credit balance, the adjustment to record bad debts for the period will require a. The percentage-of-sales method is commonly used to estimate the accounts receivable that a business expects will be uncollectible. when you use this method, use your uncollectible accounts percentage of sales small business’s past collection data to estimate what portion of the credit sales you generate each accounting period that will go unpaid. Using the percentage of sales method, they estimated that 1% of their credit sales would be uncollectible. as you can see, $10,000 ($1,000,000 * 0. 01) is determined to be the bad debt expense that management estimates to incur.
Question 1. a company uses the allowance method for estimating bad debts and has decided that 1. 5% of total sales will be uncollectible. accounts receivable has a balance of 250,000 and allowance for doubtful accounts has a $1,000 credit balance. Sales on account are $250,000, so the estimate for uncollectible accounts is $5,000 ($250,000 x. 02). the journal entry to record this is to debit bad debt expense, an income statement account, and credit allowance for uncollectible accounts, a balance sheet contra-asset account for $5,000 each. The percentage-of-net-sales method is aimed at determining the amount of uncollectible accounts expense, and the aging method is aimed at determining the balance in the account allowance for uncollectible accounts. these methods thus will show different balances in both the expense and contra-asset accounts.
Solved Uncollectible Accountspercentage Of Sales And Per
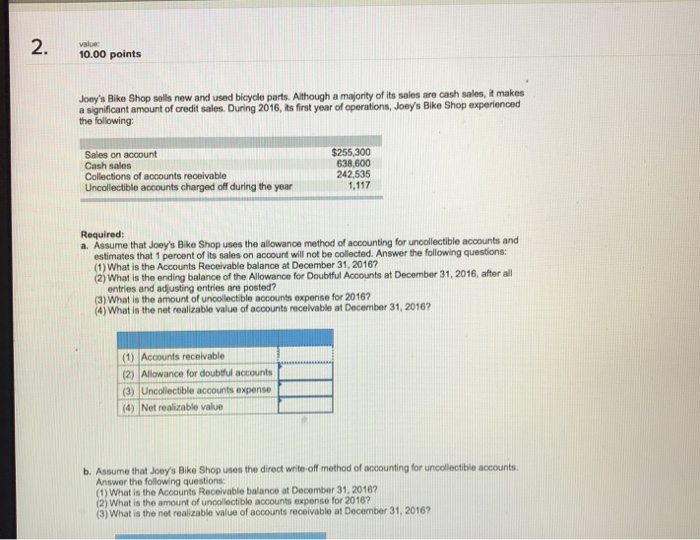
Accounting Test 2 Questions Flashcards Quizlet
Accounts receivable: $ 354,000 debit: allowance for uncollectible accounts: 610 credit: net sales: 799,000 credit. Calculate the sum of the amounts of each portion you expect will be uncollectible to calculate the total amount of uncollectible accounts. for example, calculate the sum of $750, $200, $1,050, $1,500 and $1,350. this equals $4,850 in uncollectible accounts.

Total credit sales for the year 2019: $265,000. the company has reasonable grounds to believe that 0. 5% of the total credit sales will prove to be uncollectible. required: compute the allowance for doubtful accounts for the year 2019 using sales method. Another way to estimate the amount of uncollectible accounts is to simply record a percentage of credit sales. for example, if your company and its industry has a long run experience of 0. 2% of credit sales being uncollectible, you might enter 0. 2% of each period's credit sales as a debit to bad debt expense and a credit to allowance for. For example, if the company had january credit sales of $15,000, it could estimate its uncollectible accounts receivable to be $210 ($15,000 x. 014). the. 014 is the average percentage of uncollectible accounts receivable during year 1 through year 3.
2. explanation of percentage-of-sales approach percentage-of-sales approach (income statement approach) states that the amount of bad debt expense to be recognized by a company is calculated as a percentage of credit sales generated during the current accounting period. this approach does not consider the balance in the allowance for doubtful accounts because such balance is not used in uncollectible accounts percentage of sales the.
Mckinney & co. estimates its uncollectible accounts as a percentage of credit sales. mckinney made credit sales of $1,600,000 in 2016. mckinney estimates 3. 0% of its sales will be uncollectible. at the end of the first quarter of 2017, mckinney & co. reevaluates its receivables. For example, if your company and its industry has a long run experience of 0. 2% of credit sales being uncollectible, you might enter 0. 2% of each period's credit sales as a debit to bad debt expense and a credit to allowance for doubtful accounts. Uncollectible accounts—percentage of sales and percentage of receivables. at the end of the current year, the accounts receivable account of parker's nursery supplies has a debit balance of $350,455. credit sales are $2,616,000. record the end-of-period adjusting entry on december 31, in general journal form, for the estimated uncollectible. Allowance for doubtful accounts has a debit balance of $1,240. a. the percentage of sales method is used and bad debt expense is estimated to be ¾ of 1% of credit sales. if an amount box uncollectible accounts percentage of sales does not require an entry, leave it blank.
If uncollectible accounts are expected to be 8 percent of that amount, the expense is reported as $32,000 ($400,000 × 8 percent). bad debt expense (the figure estimated) must be raised from its present zero balance to $32,000. Using the percentage-of-sales method, the estimated total uncollectible accounts are $6,622. the allowance for uncollectible accounts prior to adjustment has a debit balance of $2,935. the accounts receivable balance is $44,420.
Estimating uncollectible accounts accountants use two basic methods to estimate uncollectible accounts for a period. the first method—percentage-of-sales method—focuses on the income statement and the relationship of uncollectible accounts to sales. The percent-of-sales method for computing uncollectible accounts: computes uncollectible-account expense as a percent of accounts uncollectible accounts percentage of sales receivable. takes a balance sheet approach. employs the expense recognition (matching) concept. will result in the same amount of estimated uncollectible-accounts expense as the aging-of-receivables method. commission (puc) today urged consumers, "to be conscious of utility account security when answering telemarketing sales calls from competitive energy suppliers (suppliers) and report Solution for ervin company uses the allowance method to account for uncollectible accounts receivable. bad debt expense is established as a percentage of credit….