-Hallo friends, Accounting Methods, in the article you read this time with the title Uncollectible Accounts Income Statement Approach, we have prepared this article well for you to read and retrieve the information therein.
Hopefully the content of article posts Uncollectible, which we write this you can understand. Alright, happy reading.
Title : Uncollectible Accounts Income Statement Approach
link : Uncollectible Accounts Income Statement Approach
Uncollectible Accounts Income Statement Approach
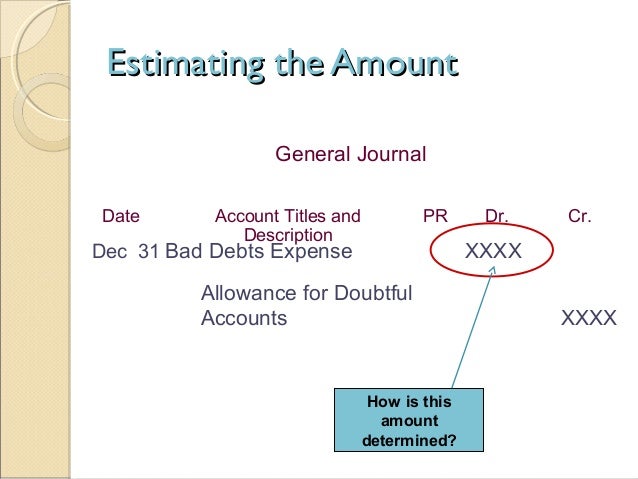
The percentage of credit sales approach focuses on the income statement and the matching principle. sales revenues of $500,000 are immediately matched with $1,500 of bad debts expense. the balance in the account allowance for doubtful accounts is ignored at the time of the weekly entries. During year 2, grande provided $104,000 of service on account. the company collected $97,000 cash from accounts receivable. uncollectible accounts are estimated to be 2% of sales on account. the amount of uncollectible accounts expense recognized on the year 2 income statement is: a) $320. b) $1,000. c) $2,080. d) $1,940. These statements are key to both financial modeling and accounting. the balance sheet displays the company’s total assets, and how these assets are financed, through either debt or equity. assets = liabilities + equity as such: the reason why this contra account is important is that it exerts no effect on the income statement accounts. 53 account for uncollectible accounts using the balance sheet and income statement approaches you lend a friend $500 with the agreement that you will be repaid in two months. at the end of two months, your friend has not repaid the money.
How To Estimate Uncollectible Accounts Dummies
Brief exercise 7-8 uncollectible accounts; income statement approach [lo5, 6] the following information relates to a company’s accounts receivable: accounts receivable balance at the beginning of the year, $315,000; allowance for uncollectible accounts at the beginning of the year, $26,500 (credit balance); credit sales during the year, $1,514,000; accounts receivable written off during the. Under this method, the uncollectible accounts expense is recognized on the basis of estimates. there are two general approaches to estimate uncollectible accounts expense. the first one is known as aging uncollectible accounts income statement approach method or balance sheet approach and the second one is known as sales method or income statement approach.
telemarketing sales calls, encourages continual review of bill statements and online account activity the pennsylvania public utility commission (puc) today Under accrual accounting, an accounts receivable is recorded on the balance sheet, and revenue is booked on the income statement. however, receivables often become uncollectible because a customer cannot or will not pay. when using the allowance for doubtful accounts method, a expense entry is recognized on the income statement, at regular. The income statement approach for estimating bad debts uses a percentage of the amount recorded for bad debt expense does not depend on the balance of the allowance for uncollectible accounts. which of the following statements is true with respect to the percentage-of-credit-sales method for estimating uncollectible accounts?.
The Balancesheet Approach To Estimate Bad Debt Bizfluent
Question: problem 7-1 uncollectible accounts; allowance method; income statement and balance sheet approach lo7-5, 7-6] swathmore clothing corporation grants its customers 30 days' credit. the company uses the allowance method for its uncollectible accounts receivable. during the year, a monthly bad debt accrual is made by multiplying 3% times the amount of credit. A simple method to account for uncollectible accounts is the direct write-off approach. under this technique, a specific account receivable is removed from the accounting records at the time it is finally determined to be uncollectible. the appropriate entry for the direct write-off approach is as follows:.
Direct Writeoff And Allowance Methods Financial Accounting

Study 66 Terms Acct200 Ch 5 Flashcards Quizlet
B. income statement approach 1. 5% of credit sales. c. balance sheet approach and the allowance for doubtful accounts should be $12,000. calculate uncollectible account expense and make required.
Accounting Tests Flashcards Quizlet
Uncollectible accounts expense allowance method.
The allowance for uncollectible accounts or allowance for doubtful accounts is a contra asset account that reduces the amount of accounts receivable to the amount that is more likely be collected. the income statement account bad debts expense is part of the adjusting entry that increases the balance in the allowance for uncollectible accounts. Problem 7-1 uncollectible accounts; allowance method; income statement and balance sheet approach lo7-5, 7-6] swathmore clothing corporation grants its customers 30 days' credit. the company uses the allowance method for its uncollectible accounts receivable. The income statement approach is an approach by which management can estimate an allowance for uncollectible receivables as a percentage of the period’s sales. an allowance as a percentage of sales is an effective approach when the company has past experience or history to use as a guide.
Study 66 terms acct200 ch. 5 flashcards quizlet.
The aging-of-receivables method of estimating uncollectible accounts is: not an acceptable method of estimating bad debts. a balance sheet approach, since it focuses on accounts receivable. an income statement approach, since it focuses on the amount of expense to be reported on uncollectible accounts income statement approach the income statement. A percentage of accounts receivable will become uncollectible for a myriad of reasons, requiring a periodic write-off of receivables. whether the allowance for doubtful accounts or the direct write off method are used, an uncollectible accounts expense must be recorded to remain compliant with u. s. gaap. below are details regarding this expense, and how it impacts the balance sheet and income. 53 account for uncollectible accounts using the balance sheet and income statement approaches. you lend a friend $500 with the agreement that you will be repaid in two months. at the end of two months, your friend has not repaid the money. This alternative computes doubtful accounts expense by anticipating the percentage of sales (or credit sales) that will eventually fail to be collected. the percentage of sales method is sometimes referred to as an income statement approach because the only number being estimated (bad debt expense) appears on the income statement.
Sales on account uncollectible accounts income statement approach are $250,000, so the estimate for uncollectible accounts is $5,000 ($250,000 x. 02). the journal entry to record this is to debit bad debt expense, an income statement account, and credit allowance for uncollectible accounts, a balance sheet contra-asset account for $5,000 each. On the income statement, bad debt expense would still be 1%of total net sales, or $5,000. in applying the percentage-of-sales method, companies annually review the percentage of uncollectible accounts that resulted from the previous year’s sales. if the percentage rate is still valid, the company makes no change. We can calculate this estimates based on sales (income statement approach) for the year or based on accounts receivable balance at the time of the estimate (balance sheet approach). as a contra asset account to the accounts receivable account, the allowance for doubtful accounts (also called allowance for uncollectible accounts or allowance for. Calculate allowance for doubtful accounts using sales method or income statement approach. prepare adjusting entry to recognize uncollectible accounts expense and to update the allowance for doubtful accounts account at the end of the year 2015. solution: (1). allowance for doubtful accounts: $175,000 × 0. 01 = $1,750 (2).
The first is an income-statement approach that measures bad debt as a percentage of sales. the second is a balance-sheet approach that measures uncollectibles as a percentage of ending accounts receivable. under the balance-sheet approach, the company looks at historical data and estimates uncollectible accounts income statement approach what percentage of receivables ends up being uncollectible. The income statement approach for estimating bad debts uses a percentage of. the amount recorded for bad debt expense does not depend on the balance of the allowance for uncollectible accounts. which of the following statements is true with respect to the percentage-of-credit-sales method for estimating uncollectible accounts?.