-Hallo friends, Accounting Methods, in the article you read this time with the title An Uncollectible Accounts Expense, we have prepared this article well for you to read and retrieve the information therein.
Hopefully the content of article posts Uncollectible, which we write this you can understand. Alright, happy reading.
Title : An Uncollectible Accounts Expense
link : An Uncollectible Accounts Expense
An Uncollectible Accounts Expense
The uncollectible accounts expense account shows the company estimates it cost $750 in january to sell to customers who will not pay. the accounts receivable account shows the company's customers owe it $50,000. the allowance for uncollectible accounts shows the company expects its customers to be unable to pay $750 of the $50,000 they owe. Accounts written off as uncollectible during 2017 500 bad expense is estimated by the aging-of-receivables method. management estimates that $2,850 of accounts receivable will be uncollectible. calculate the amount of net accounts receivable after the adjustment for bad debts. a. $19,150 b. $20,150 c. $18,150 d. $17,650.
How To Estimate Uncollectible Accounts Dummies
Accounts uncollectible are loans, receivables or other debts that have virtually no chance of being paid. an account may become uncollectible for many reasons, including the debtor's bankruptcy. Allowance for doubtful accounts has a debit balance of an uncollectible accounts expense $500 at the end of the year (before adjustments), and the uncollectible accounts expense is estimated at 3% of net sales. if net sales are $600,000, the amount of the adjusting entry to record the provision for doubtful accounts is. Allowance for doubtful accounts: an allowance for doubtful accounts is a contra-asset account that reduces the total receivables reported to reflect only the accounts receivable expected to be.

A percentage of accounts receivable will become uncollectible for a myriad of reasons, requiring a periodic write-off of receivables. whether the allowance for doubtful accounts or the direct write off method are used, an uncollectible accounts expense must be recorded to remain compliant with u. s. gaap. below are details regarding this expense, and how it impacts the balance sheet and income. The projected bad debt expense is properly matched against the related sale, thereby providing a more accurate view of revenue and expenses for a specific period of time. in addition, this accounting process prevents the large swings in operating results when uncollectible accounts are written off directly as bad debt expenses.
Uncollectible accounts expense allowance method.
Accounting For Uncollectible Accounts Receivable Part 1

The offsetting debit is to an expense account: uncollectible accounts expense. while the direct write-off method is simple, it is only acceptable in those cases where bad debts are immaterial in amount. in accounting, an item is deemed material if it is large enough to affect the judgment of an informed financial statement user. Accountsuncollectible are loans, receivables or other debts that have virtually no chance of being paid. an account may become uncollectible for many reasons, including the debtor's bankruptcy. Recording uncollectible accounts expense and bad debts. november 14, 2018 november 3, 2018 by rashidjaved. the risk of extending credit arises from the possibility that the customer will not pay. this risk impacts both the measurement of income and an uncollectible accounts expense the description of the receivables held by the seller. the accountant’s task involves. Later, when a specific account receivable is actually written off as uncollectible, the company debits allowance for doubtful accounts and credits accounts receivable. the allowance method is preferred over the direct write-off method because: the income statement will report the bad debts expense closer to the time of the sale or service, and.
How To Estimate Uncollectible Accounts Dummies
Uncollectibleaccountsexpense is the charge made to the books when an uncollectible accounts expense a customer defaults on a payment. this expense can be recognized when it is certain that a customer will not pay. a more conservative approach is to charge an estimated amount to expense when a sale is made; doing so matches the expense to the related sale within the same reporting period. Allowance for doubtful accounts primarily means creating an allowance for the estimated part of the accounts that may be uncollectible and may become bad debt and is shown as a contra asset account that reduces the gross receivables on the balance sheet to reflect the net amount that is expected to be paid. Calculate the sum of the amounts of each portion you expect will be uncollectible to calculate the total amount of uncollectible accounts. for example, calculate the sum of $750, $200, $1,050, $1,500 and $1,350. this equals $4,850 in uncollectible accounts.
Sales on account are $250,000, so the estimate for uncollectible accounts is $5,000 ($250,000 x. 02). the journal entry to record this is to debit bad debt expense, an income statement account, and credit allowance for uncollectible accounts, a balance sheet contra-asset account for $5,000 each. Once this account is identified as uncollectible, the company will record a reduction to the customer’s accounts receivable and an increase to bad debt expense for the exact amount uncollectible. under generally accepted accounting principles ( gaap ), the direct write-off method is not an acceptable method of recording bad debts, because it. The uncollectible accounts expense (debited in the above entry) is closed into income summary account like any other expense account and the allowance for doubtful accounts (credited in the above entry) appears in the balance sheet as a deduction from the face value of accounts receivable.

Allowance For Doubtful Accounts Definition
Uncollectible accounts expense — accountingtools.
How Do I Calculate Uncollectible Accounts Bizfluent
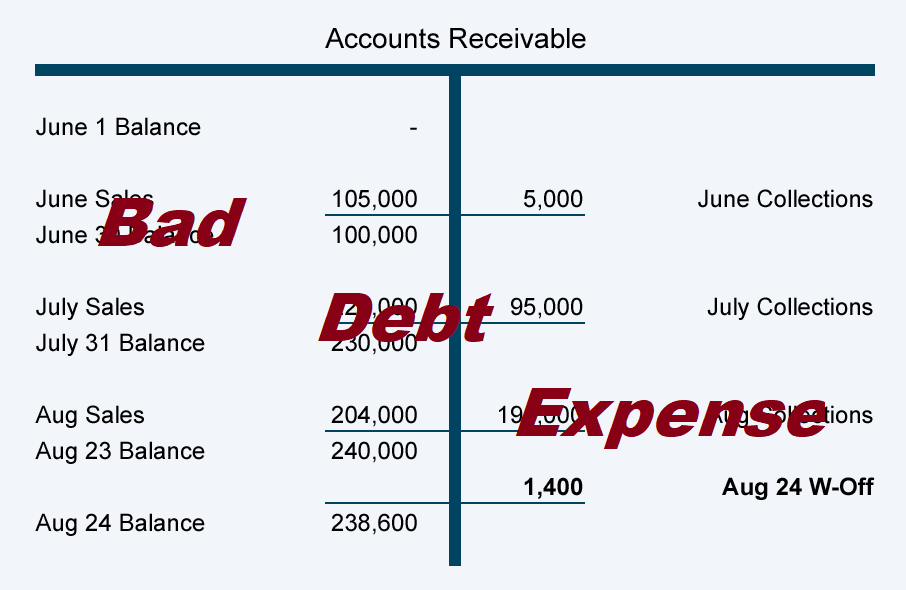
The allowance method of recognizing uncollectible accounts expense follows the matching principle of accounting i. e. it recognizes uncollectible accounts expense in the period in which the related sales are made. under this method, the uncollectible accounts expense is recognized on the basis of estimates. there are two general approaches to estimate uncollectible accounts expense. Accounting equation 06. accounting principles 07. financial accounting 08. adjusting entries 09. financial statements 10. balance sheet 11. working capital and liquidity 12. income statement 13. cash flow statement 14. financial ratios 15. bank reconciliation 16. accounts receivable and bad debts expense 17. accounts payable 18.
A percentage of accounts receivable will become uncollectible for a myriad of reasons, requiring a periodic write-off of receivables. whether the allowance for doubtful accounts or the direct write off method are used, an uncollectible accounts expense must be recorded to remain compliant with u. s. gaap. Accounts receivable and bad debts expense 17. accounts payable 18. inventory and cost of goods sold 19. depreciation 20. payroll accounting 21. bonds payable 22. stockholders' equity 23. present value of a single amount 24. present value of an ordinary annuity 25. future value of a single amount 26. nonprofit accounting 27. A account receivable that has previously been written off may subsequently be recovered in full or in part. it is known as recovery of uncollectible accounts or recovery of bad debts. this article briefly explains the accounting treatment when a previously written off account is recovered and the cash is received from the related receivable.
Accounts receivable is known as a control account. this means the total of all individual accounts found in the subsidiary ledger must equal the total balance in accounts receivable. the allowance method uses an estimate of uncollectible expense, also known as bad debts expense, and does not predict which individual accounts will be written off. The debit to bad debts expense would report credit losses of $50,000 on the company’s june income statement. above, we assumed that the allowance for doubtful accounts began with a balance of zero. if instead, the allowance for uncollectible accounts began with a balance of $10,000 in june, we would make the following adjusting entry instead:. A disadvantage to the direct write-off method of recording uncollectible accounts expense is that the expense may not be recorded in the same fiscal period as the revenue for sale true recording uncollectible accounts expense in the same fiscal period in which the original sale on account was made is an application of the matching expenses with.
Notice that the preceding entry reduces the receivables balance for the item that is uncollectible. the offsetting debit is to an expense account: uncollectible accounts expense. while the direct write-off method is simple, it is only acceptable in those cases where bad debts are immaterial in amount. Uncollectible accounts expense is the charge made to the books when a customer defaults on a payment. this expense can be recognized when it is certain that a customer will not pay. a more conservative approach is to charge an estimated amount to expense when a an uncollectible accounts expense sale is made; doing so matches.